Geogrids are widely used materials in civil engineering, mainly used to enhance soil structure, control soil erosion and provide stability. Geogrids can be divided into many types according to different manufacturing processes and material properties. Here we mainly introduce four common geogrids: bidirectional geogrid, fiberglass geogrid, polyester geogrid and unidirectional geogrid.
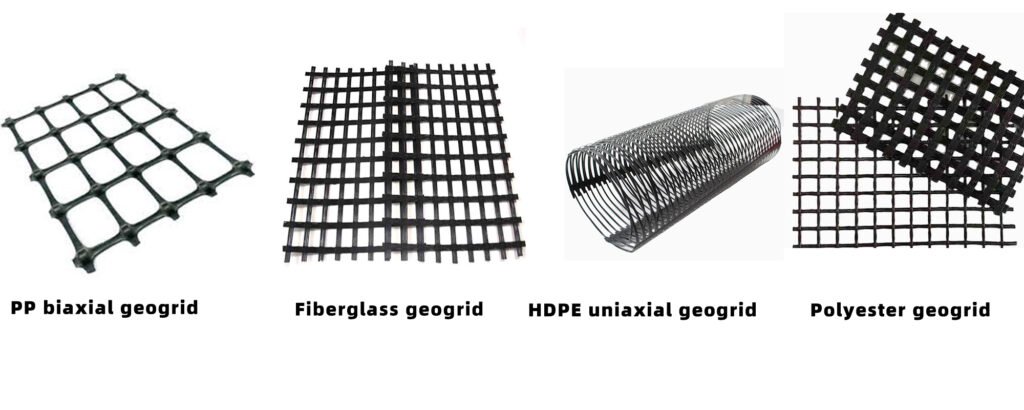
PP Biaxial Geogrid is a biaxial geogrid made of polypropylene (PP) resin. It forms a high-strength grid structure through a heating and stretching process, and the grid in each direction has a high tensile strength.
Features;
- High strength: It has high tensile strength in both directions and can effectively enhance the soil structure.
- Corrosion resistance: Polypropylene material has good chemical stability and can resist corrosion in a variety of environments.
- Anti-aging: After special treatment, it has excellent anti-ultraviolet and anti-aging properties, extending the service life.
- Flexibility: It has a certain flexibility, which is convenient for construction and adaptability to different terrain conditions.
- Lightweight: It is light in weight, easy to transport and install, and reduces construction costs.
- Temperature resistance: It can maintain stable performance in a wide temperature range.

Fiberglass geogrid is a flat mesh structure material made of alkali-free glass fiber through a special process. It has extremely high tensile modulus, low elongation at break and good corrosion resistance.
Features
- High strength: It has extremely high tensile strength in both directions and can withstand large loads.
- Low elongation: It has low elongation at break and can maintain high stability when subjected to force.
- Corrosion resistance: The glass fiber material has excellent chemical stability and can resist corrosion in a variety of environments.
- High temperature resistance: It can maintain stable performance in high temperature environments.
- Aging resistance: After special treatment, it has good UV resistance and aging resistance, extending the service life.
- Lightweight: It is light in weight, easy to transport and install, and reduces construction costs.
- Good compatibility: It can be well combined with a variety of soil types and filling materials.
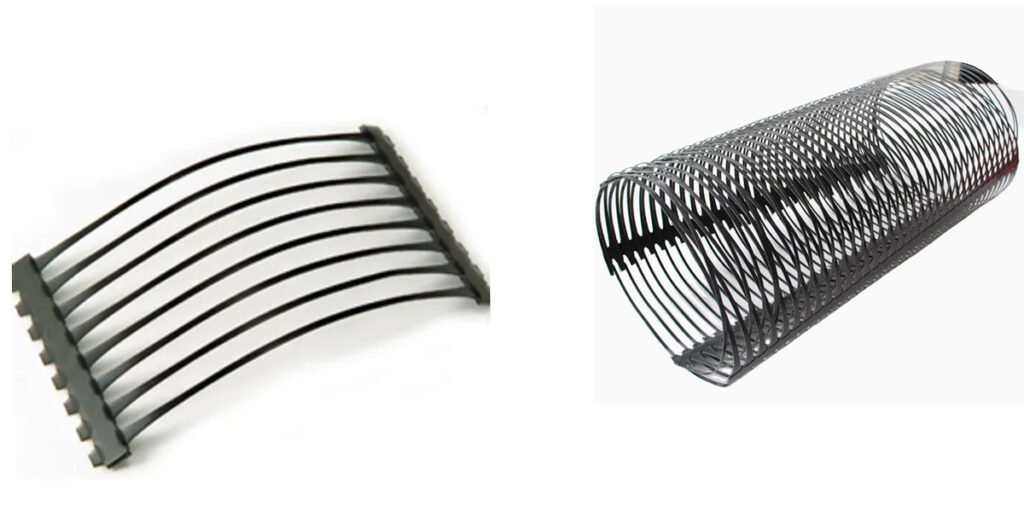
HDPE Uniaxial Geogrid is a unidirectional geogrid made of high-density polyethylene (HDPE) resin. It forms a high-strength grid structure through heating and stretching processes, and has high tensile strength mainly in one direction.
Features
- High strength: It has extremely high tensile strength in one direction and can effectively enhance the soil structure.
- Corrosion resistance: HDPE material has good chemical stability and can resist corrosion in a variety of environments.
- Anti-aging: After special treatment, it has excellent anti-ultraviolet and anti-aging properties, extending the service life.
- Flexibility: It has a certain flexibility, which is convenient for construction and adaptability to different terrain conditions.
- Lightweight: It is light in weight, easy to transport and install, and reduces construction costs.
- Temperature resistance: It can maintain stable performance in a wide temperature range.

Polyester Geogrid is a geogrid made of polyester (PET) fibers through weaving or knitting processes. It has high tensile strength, good corrosion resistance and aging resistance, and is suitable for a variety of civil engineering applications.
Features
- High strength: It has high tensile strength in both directions and can effectively enhance the soil structure.
- Low elongation: It has low elongation at break and can maintain high stability when subjected to force.
- Corrosion resistance: Polyester material has good chemical stability and can resist corrosion in a variety of environments.
- Aging resistance: After special treatment, it has excellent anti-UV and anti-aging properties, extending the service life.
- Flexibility: It has a certain flexibility, which is convenient for construction and adaptability to different terrain conditions.
- Lightweight: It is light in weight, easy to transport and install, and reduces construction costs.
- Good compatibility: It can be well combined with a variety of soil types and filling materials.
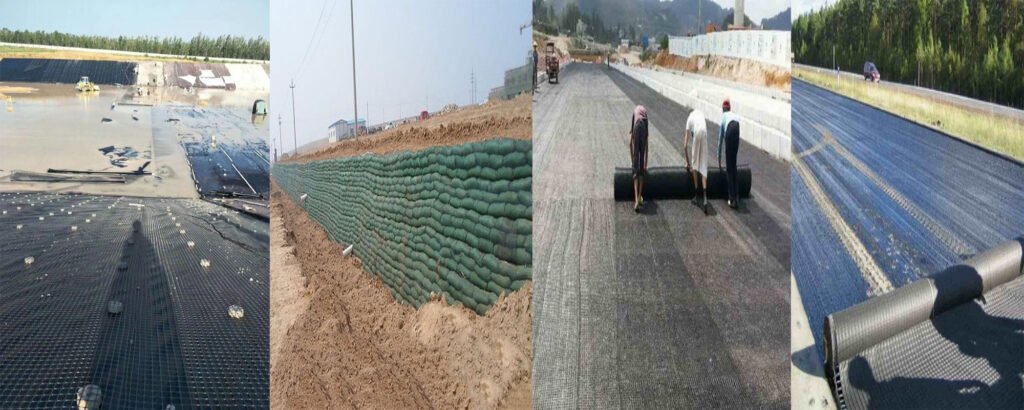
Geogrid Application Areas
- Highway construction
Improve bearing capacity: By laying geogrids in the roadbed, the bearing capacity of the road base can be significantly improved and the road surface settlement can be prevented.
Reduce uneven settlement: Geogrids can evenly distribute the load and reduce road cracks caused by uneven settlement. - Slope protection
Prevent landslides: Laying geogrids on the road slopes can increase the stability of the slopes and prevent landslides and soil erosion.
Vegetation restoration: Combined with vegetation planting, geogrids can provide a stable growth environment and promote the ecological restoration of the slopes. - Drainage system
Improve drainage performance: Geogrids can be used as part of the drainage layer to improve the drainage performance of the soil and reduce the impact of moisture on the roadbed. - Railway construction
Strengthen track foundation: Laying geogrids in the railway track bed can enhance the stability of the track foundation and reduce maintenance costs.
Prevent ballast loss: Geogrids can prevent ballast from being lost during train operation and keep the track in good condition. - Bridge bearing area
Enhance stability: Laying geogrids in the bridge bearing area can enhance the stability of the bridge bearing and extend the service life of the bridge. - Airport construction runway foundation reinforcement
Improve bearing capacity: Laying geogrids in the foundation of the airport runway can improve the foundation bearing capacity of the runway and ensure the safety of aircraft takeoff and landing.
Reduce settlement: Geogrids can reduce the settlement of the runway and maintain the flatness of the runway. - Water conservancy project dam reinforcement
Enhance stability: Laying geogrids in the dam can enhance the stability of the dam and prevent damage caused by flood scouring.
Prevent leakage: Geogrids can be used in combination with anti-seepage materials to prevent leakage of the dam. - Reservoir slope protection
Prevent erosion: Laying geogrids on the slope of the reservoir can prevent slope erosion and improve the safety of the reservoir.
Ecological restoration: Combined with vegetation planting, geogrids can promote the ecological restoration of the reservoir slope. - Construction Engineering
Improve bearing capacity: Laying geogrids in soft soil foundations can improve the bearing capacity of the foundation and reduce the settlement of buildings.
Uniformly distribute loads: Geogrids can evenly distribute the load of buildings and improve the overall stability of the foundation. - Retaining wall
Enhance stability: Laying geogrids behind retaining walls can enhance the stability of retaining walls and prevent wall collapse.
Reduce lateral pressure: Geogrids can reduce the lateral pressure of soil on retaining walls and improve the safety of retaining walls. - Landfill
Impermeability and reinforcement: Laying geogrids in landfills can prevent pollutant leakage and enhance the stability of landfills.
Extend service life: Geogrids can extend the service life of landfills and reduce environmental pollution. - Ecological restoration
Soil reinforcement: In ecological restoration projects, geogrids can be used for soil reinforcement to prevent soil erosion.
Vegetation restoration: Combined with vegetation planting, geogrids can provide a stable growth environment and promote ecological restoration. - Agricultural Engineering
Improve Soil Quality: Laying geogrids in agricultural land can improve soil structure and improve soil quality.
Prevent Erosion: Geogrids can prevent soil erosion in farmland and protect the growth environment of crops. - Tailing Pond Reinforcement
Enhance Stability: Laying geogrids in tailings ponds can enhance the stability of tailings ponds and prevent tailings leakage.
Reduce Pollution: Geogrids can reduce the pollution of tailings ponds to the environment and improve the safety of mining projects. - Ports and Wharfs
- Improve Carrying Capacity: Laying geogrids in the foundations of ports and wharves can improve the bearing capacity of the foundation and ensure the safety of facilities.
Reduce Settlement: Geogrids can reduce the settlement of the foundation and maintain the stability of ports and wharves. - Bank Protection Engineering
Prevent Erosion: Laying geogrids on both sides of the river can prevent riverbank erosion and protect the ecological environment along the coast.
Ecological Restoration: Combined with vegetation planting, geogrids can promote ecological restoration on both sides of the river.

Geogrids have the advantages of high strength, corrosion resistance, and anti-aging, and play an important role in many civil engineering fields. From roads, railways, airports to water conservancy projects, construction projects, environmental protection projects and other fields, geogrids can effectively improve the quality and safety of engineering projects. When selecting and using them, they should be reasonably matched according to specific engineering needs and site conditions to give full play to their advantages.

