Nonwoven geotextile vs woven geotextile difference between : Choose the best geotextile to improve engineering results
Geotextile, as an important material in the field of civil engineering and environmental protection, plays a vital role in multiple application scenarios. Used in road construction, dam reinforcement, drainage system, landfill anti-seepage, geotextile can play multiple functions such as strengthening structure, improving water flow control, and improving stability. Among geotextile products, non-woven geotextile and woven geotextile are the two most widely used types. Both geotextiles are used to strengthen soil structure, and there are significant differences in materials, manufacturing processes, performance characteristics and applicable scenarios. Understanding the difference between the two will help choose the best geotextile to improve engineering results.
Nonwoven geotextile vs woven geotextile
Non-woven geotextile
Non-woven geotextile is a geotextile made by weaving short or long fibers through mechanical, chemical or thermal bonding processes. The traditional weaving process is not required, and the fibers are connected into a non-woven structure by pressing, hot bonding or needle punching. The structure of non-woven geotextile is usually loose, with good water permeability, filterability and flexibility, suitable for scenes requiring high water permeability and flexibility.
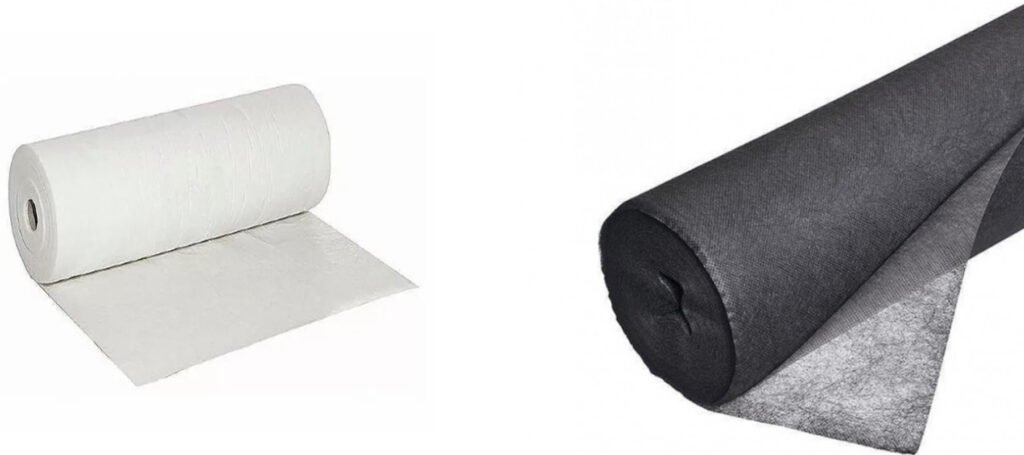

Woven geotextile
Woven geotextile is a layer of solid geotextile made by weaving long fibers (usually polyester or polypropylene fibers) through traditional weaving processes. Woven geotextile has a tighter structure, and the weaving method can be plain weave, twill weave or other complex weaving forms. Woven geotextile generally has higher tensile strength and lower water permeability, and is suitable for projects requiring higher strength and tensile properties.

Difference in manufacturing process
Manufacturing process of non-woven geotextile;
- Needle punching process: Use special machinery to punch fibers into the fabric through needle punching process to form a strong mesh structure.
- Thermal bonding process: The fibers are combined together through hot melt treatment to form a fabric. This process makes the non-woven fabric have good toughness and softness.
- Chemical bonding process: The fibers are bonded by chemical adhesives, which is suitable for some special needs, such as applications that require higher chemical resistance or waterproof performance.
Manufacturing process of woven geotextile
- Woven geotextile uses traditional weaving technology to weave fibers (usually long fibers) into cloth through the interlacing of warp and weft yarns. Its manufacturing process includes:
- Plain weave: uses a simple cross structure.
- Twill weave: uses a more complex cross structure to make the fabric stronger.
- Complex weave: A weaving method designed according to specific needs to improve the strength and durability of the fabric.
Scope of application and application scenarios
Scope of application of non-woven geotextiles;
- Road and railway construction: used for drainage and soil reinforcement.
- Landfill: used for anti-seepage, isolation and drainage systems.
- Dam and soil and water conservation: used to prevent soil erosion and stabilize soil.
- Agricultural field: such as farmland drainage, soil covering, green belts, etc.
- Mining engineering: used for drainage and isolation of mine leachate.

Scope of application of woven geotextiles
- Roadbed reinforcement: used for high-intensity projects such as roads, railways and airport runways, which can improve soil bearing capacity.
- Slope reinforcement: used to prevent slope landslides and soil erosion, and increase slope stability.
- Ports and dams: enhance the stability of the structure and withstand large loads.
- Civil engineering construction: used for building foundations and bridge foundations that withstand high loads.

Choice between non-woven geotextile and woven geotextile;
Choose according to project requirements
- High-intensity projects: If the project needs to withstand large tensile forces and mechanical pressures, woven geotextiles will be a more appropriate choice. For example, large-scale soil stabilization projects in infrastructure construction.
- Permeability requirements: If the project requires good permeability and filtration, especially drainage systems, soil and water conservation, landfills, etc., it is recommended to choose non-woven geotextiles.
- Environmental adaptability
- Irregular terrain: Non-woven geotextiles are more flexible and suitable for use on irregular terrain, and can better adapt to terrain changes.
- Long-term use: Woven geotextiles are suitable for long-term use, especially in environments with large loads and high-intensity pressures.
- Cost and benefits
- Short-term use: Non-woven geotextiles have a relatively low cost and are suitable for short-term projects.
- Long-term use: Although woven geotextiles have a higher initial cost, their durability and tensile strength make them suitable for long-term, high-intensity projects.
Non-woven geotextiles and woven geotextiles each have their own characteristics and advantages, and are suitable for different engineering needs. Non-woven geotextiles are excellent in permeability, flexibility and tear resistance, and are suitable for projects that require drainage, filtration, isolation and other functions; while woven geotextiles have obvious advantages in tensile strength, durability and stability, and are suitable for high-load applications such as soil reinforcement and road construction. By understanding their differences and characteristics, you can better choose the right geotextile to improve the effect and quality of the project. If you need to customize or purchase other geosynthetics products, please feel free to contact our professional team.